The U.S. Supreme Court’s decision in United States v. The Amistad on March 9, 1841, was a pivotal moment in American legal history, addressing issues of slavery, international law, and human rights. The case involved a group of Africans who had been illegally enslaved,…
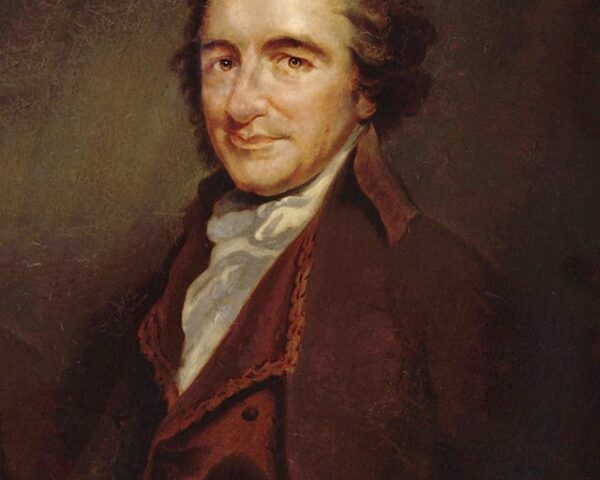
Read MoreOn March 8, 1775—barely six weeks before the first shots of the American Revolution—a small but incendiary essay appeared in the Pennsylvania Journal and Weekly Advertiser. The piece carried no author’s name. Its title, however, left little doubt about its subject: “African Slavery in…
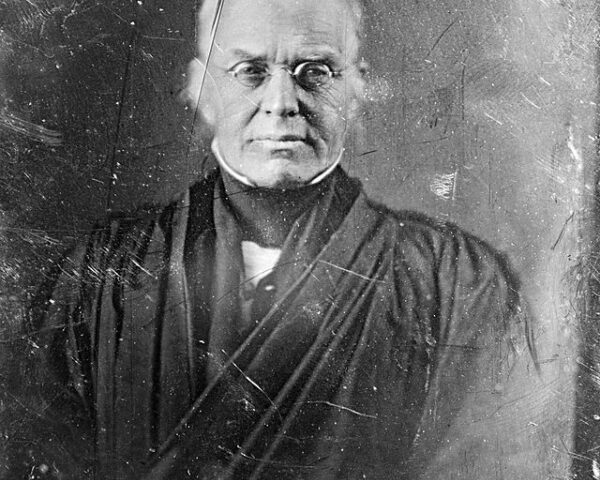
Read MoreOn March 7, 1850, Senator Daniel Webster of Massachusetts delivered one of the most significant speeches in American history, later known as the “Seventh of March” speech. Speaking at a time of deep national division, Webster endorsed the Compromise of 1850, a contentious set…
Read MoreIn 1807, Congress passed a law banning the international slave trade to the United States, set to take effect at the start of 1808, as permitted by the Constitution. The debate over this legislation was influenced by economic interests, national security concerns, and fears…
Read MoreAbraham Lincoln’s Cooper Union address, delivered on February 27, 1860, in New York City, stands as one of the most legendary speeches ever given by an American politician. At the time, the United States was deeply divided over the issue of slavery, and the…
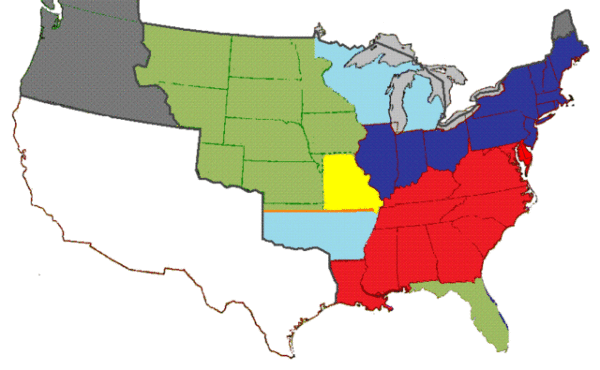
Read MoreOn February 17, 1820, hoping to end the question of the future of slavery in the United States, Congress introduced the Missouri Compromise. Henry Clay, a prominent statesman, orchestrated the compromise with the intent of preserving harmony in the Union by delicately balancing the…
Read MoreOn February 6, 1820, a small group of 86 African American emigrants departed New York aboard the ship Elizabeth, embarking on a journey that would bind the future of the United States to the West African coast in complicated and enduring ways. Sponsored by…
Read MoreOn February 1, 1865, Abraham Lincoln affixed his signature to the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, completing the final executive step in abolishing slavery throughout the nation. The act itself—quiet, procedural, and almost anticlimactic—belied the enormity of its meaning. With a few…
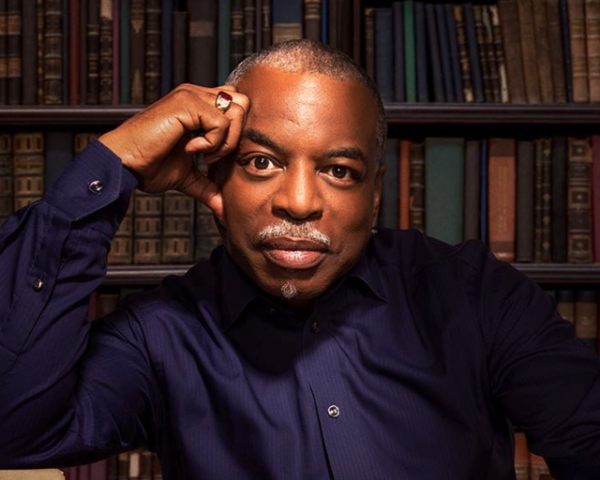
Read MoreIt is considered one of the most important television miniseries of all time. On January 23, 1977, “Roots” debuted, marking a watershed moment in the history of American TV. Based on Alex Haley’s novel, the miniseries chronicled the journey of an African-American family, beginning…
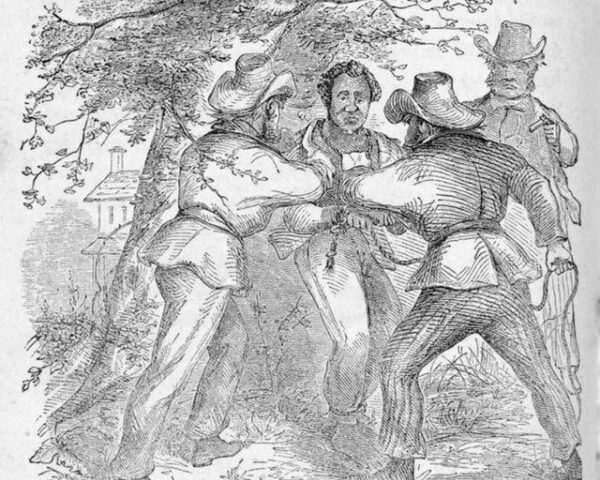
Read MoreIn January 4, 1853, Solomon Northup finally breathed the sweet air of freedom again. Northup was an African-American man born in July 1808 in Minerva, New York. Born a free man in a time when slavery was still legal in the United States, Northup…
Read More